AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are among the most powerful technologies shaping the modern digital landscape. From virtual assistants and recommendation engines to autonomous vehicles and advanced medical diagnostics, these technologies are influencing almost every industry. Despite their widespread adoption, many people still struggle to understand the differences between these terms and often use them interchangeably.
According to IBM Artificial Intelligence, Artificial Intelligence is the broader concept of creating machines that can simulate human intelligence, while Machine Learning and Deep Learning are specific approaches used to build such systems. Understanding how these technologies differ is essential for developers, students, and businesses aiming to work with AI-driven solutions effectively.
This blog explains Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning in a clear and practical way, focusing on their definitions, differences, real-world applications, and career relevance.
Table of Contents
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
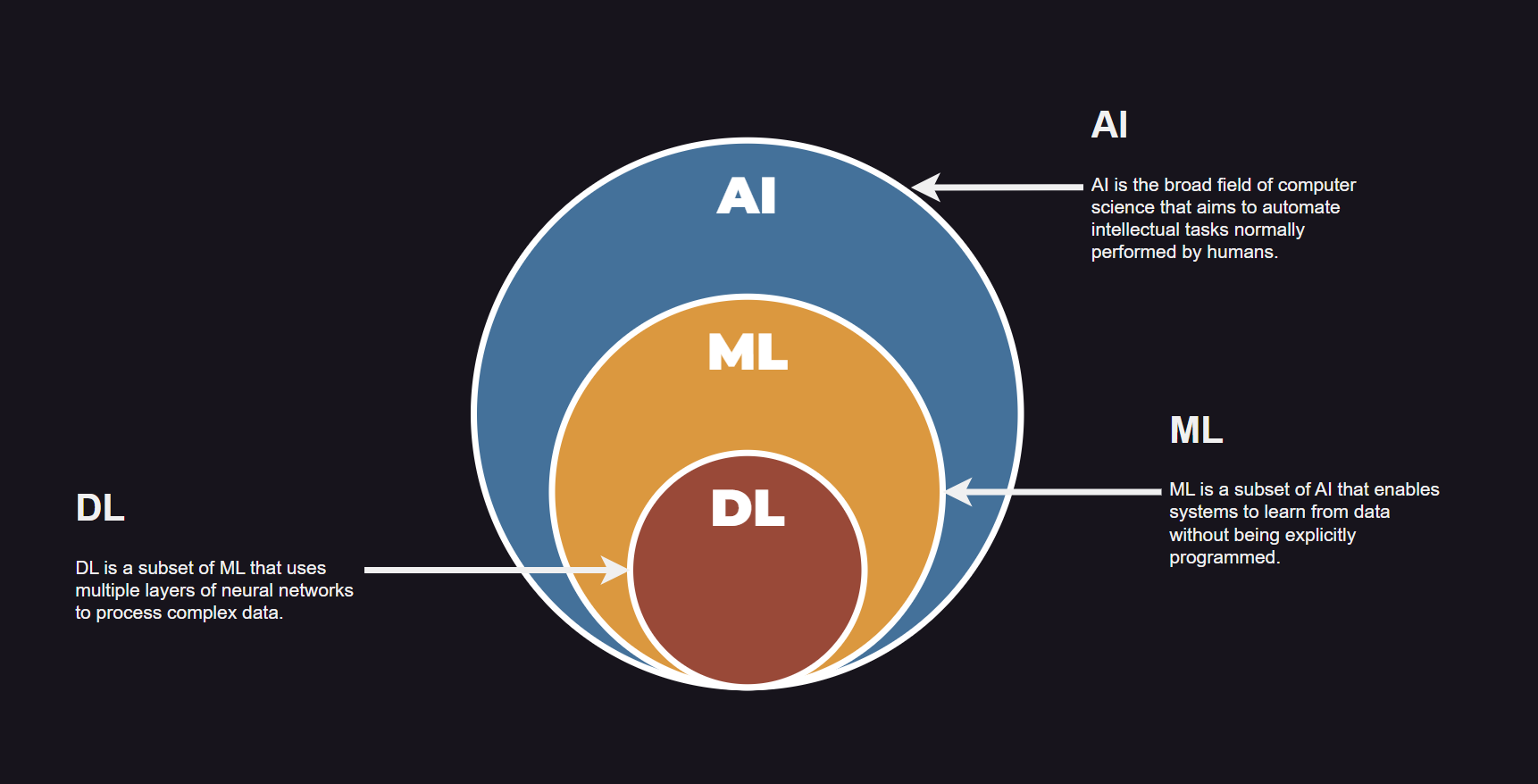
Artificial Intelligence refers to the capability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, problem-solving, decision-making, language understanding, and visual perception. The goal of AI is to create systems that can think and act intelligently in real-world environments.
As explained in IBM AI documentation, Artificial Intelligence is an umbrella term that includes both rule-based systems and learning-based models. This means that not all AI systems rely on data or learning algorithms. Some AI applications work by following predefined rules created by humans.
AI is widely used in chatbots, recommendation systems, robotic process automation, fraud detection, and expert systems. These applications help organizations automate tasks, improve accuracy, and enhance user experiences across digital platforms.
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence that enables systems to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of writing rules manually, developers train Machine Learning models using data so that the system can identify patterns and make predictions on its own.
According to the Google Machine Learning Crash Course, Machine Learning allows computers to learn from experience and improve performance automatically. This makes ML highly effective for solving complex problems where defining rules manually is impractical.
Machine Learning is commonly used in email spam filtering, product recommendations, predictive analytics, credit scoring, and speech recognition. As more data becomes available, these systems continue to improve their accuracy.
Types of Machine Learning
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning uses labeled datasets to train models. It is widely applied in image classification, sentiment analysis, and email spam detection.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns. It is often used for customer segmentation and anomaly detection.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning trains models through rewards and penalties. It is commonly used in robotics, game AI, and autonomous systems.
A detailed overview of these approaches is available in Google’s Machine Learning Guides.
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is an advanced subset of Machine Learning that uses artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain. These networks contain multiple layers that allow systems to learn complex patterns from large amounts of data.
According to NVIDIA Deep Learning resources, Deep Learning has driven major breakthroughs in computer vision, natural language processing, and speech recognition. Unlike traditional Machine Learning models, Deep Learning systems automatically extract features from raw data, reducing the need for manual feature engineering.
Deep Learning is used in facial recognition, voice assistants, medical imaging analysis, and self-driving car technologies. These systems typically require large datasets and high-performance hardware such as GPUs.
Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch are widely used to develop and deploy Deep Learning models.
AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
Artificial Intelligence represents the broad goal of building intelligent machines. Machine Learning is a practical method within AI that enables systems to learn from data. Deep Learning is a specialized technique within Machine Learning that focuses on neural networks and complex data processing.
AI systems may function with or without data, while Machine Learning depends heavily on structured datasets. Deep Learning requires massive volumes of data and significant computational resources to achieve high accuracy.
In terms of human involvement, AI systems may rely on manually defined rules, Machine Learning models require some feature engineering, and Deep Learning models minimize human intervention by learning features automatically.
A technical comparison can be explored in IBM’s AI vs ML vs DL overview.
Career Opportunities in AI, ML, and Deep Learning
The demand for AI-related skills continues to grow globally. According to the World Economic Forum Future of Jobs Report, roles related to Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are among the fastest-growing careers.
Common job roles include Artificial Intelligence Engineer, Machine Learning Engineer, Data Scientist, and Deep Learning Specialist. These careers require strong skills in programming, mathematics, and data analysis.
Learning platforms such as Coursera Artificial Intelligence Courses and Khan Academy Computer Science offer reliable learning paths for beginners and professionals.
Which Technology Should You Learn First?
Beginners are advised to start with Artificial Intelligence fundamentals, then move on to Machine Learning, and finally explore Deep Learning. Building a strong foundation in Python, statistics, and linear algebra is essential.
Official resources like Python Documentation and NumPy Documentation are excellent for strengthening core skills.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are interconnected technologies driving innovation across industries. Artificial Intelligence defines the vision of intelligent systems, Machine Learning enables data-driven learning, and Deep Learning allows machines to solve highly complex problems.
Understanding these differences helps developers choose the right tools, businesses adopt effective solutions, and students plan successful careers. As AI continues to evolve, mastering these technologies will remain a valuable skill for the future.
Also Check Powerful Web Security Basics 2026 – Protect Web from Attacks
1 thought on “Comparision between AI, ML and DL – Powerful Guide – 2026”